We assessed patterns of landscape connectivity in 16 native amphibian species grouped in four communities in the most populated region in Spain (Community of Madrid). Leer más.
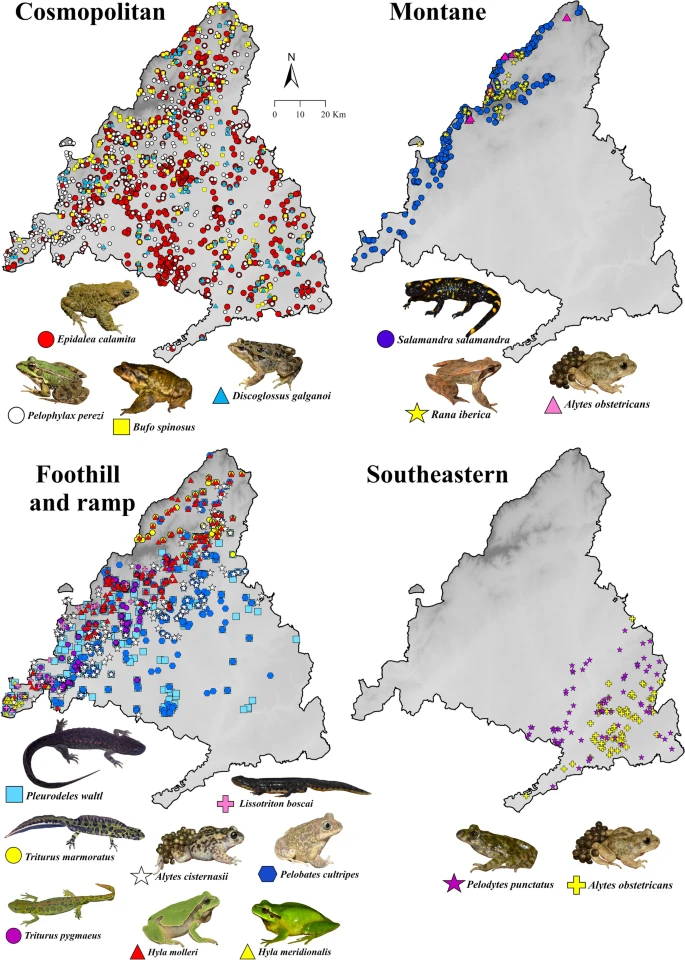






We assessed patterns of landscape connectivity in 16 native amphibian species grouped in four communities in the most populated region in Spain (Community of Madrid). Leer más.

Our results showed no evidence of Rv or Bsal, but Bd was detected with low to moderate infection loads. Leer más.
By analysing samples from a broad spectrum of the T. hermanni distribution range, we have further shown that SNPSTR markers can be used to identify the subspecies and the geographical origin with a high degree of certainty. Leer más.
None of the sampled individuals exhibited clinical signs of chytridiomycosis. Despite the extensive global research on Bd, this study represents the first report of this fungus in amphibian populations in Mauritius. Leer más.
We carried out multilocus phylogenetic analyses using three mitochondrial and three nuclear markers and analysis of morphological data to verify whether the undescribed lineage deserves a species rank. Leer más.
