Our findings open new avenues into genomic mechanisms of resilience across spatially heterogeneous environments and how rapid evolution correlates with extreme weather events associated with climate change. Leer más.







Our findings open new avenues into genomic mechanisms of resilience across spatially heterogeneous environments and how rapid evolution correlates with extreme weather events associated with climate change. Leer más.

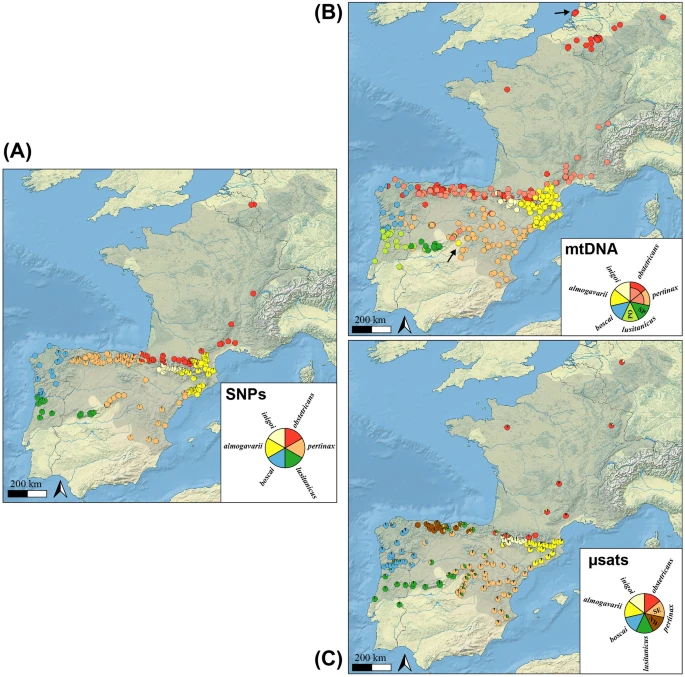
Our results should be considered in future red list assessments, management unit delimitation, and ex-situ conservation efforts, and are also relevant to study chytrid epidemiology, for which A. obstetricans has been a model organism for nearly three decades. Leer más.
We found significant warming at 33 nesting locations, 23 of which also showed significant increases in nest counts. Our results suggest that rising temperatures may be boosting nest numbers in regions of the Caribbean, Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean (sites in Cayman, Mexico, Brazil, Cyprus and Turkey). Leer más.

The degree of differentiation between species is congruent with the absence of hybridization and the precise pattern of change suggests that differences in head form could be, at least in part, adaptive. Leer más.

In this study, we identified the main drivers influencing amphibian species richness by conducting a comprehensive ecological characterization in 201 ponds across seven European countries spanning a large latitudinal and longitudinal gradient. Leer más.
