Publicación de las III jornadas para la conservación de anfibios: Seguimiento de poblaciones amenazadas. Sociedad de Ciencias Aranzadi. Ir a la página de On-line first para descargar los artículos.







Publicación de las III jornadas para la conservación de anfibios: Seguimiento de poblaciones amenazadas. Sociedad de Ciencias Aranzadi. Ir a la página de On-line first para descargar los artículos.

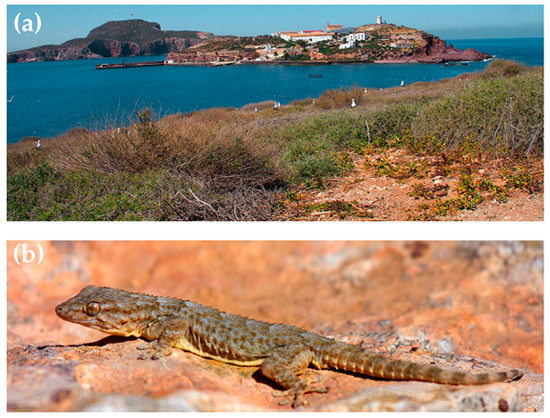
Results showed that seminatural habitats differed from actual natural habitats in some microhabitat characteristics and in diversity of available prey. The diet of geckos also differed between habitats, being less diverse in altered habitats. However, the health state (body condition) of geckos was similar between habitats. These geckos seem able to modify their diet selection patterns to cope with anthropic disturbances of the habitat, which would allow them to inhabit and prosper in human-altered ecosystems. Leer más.

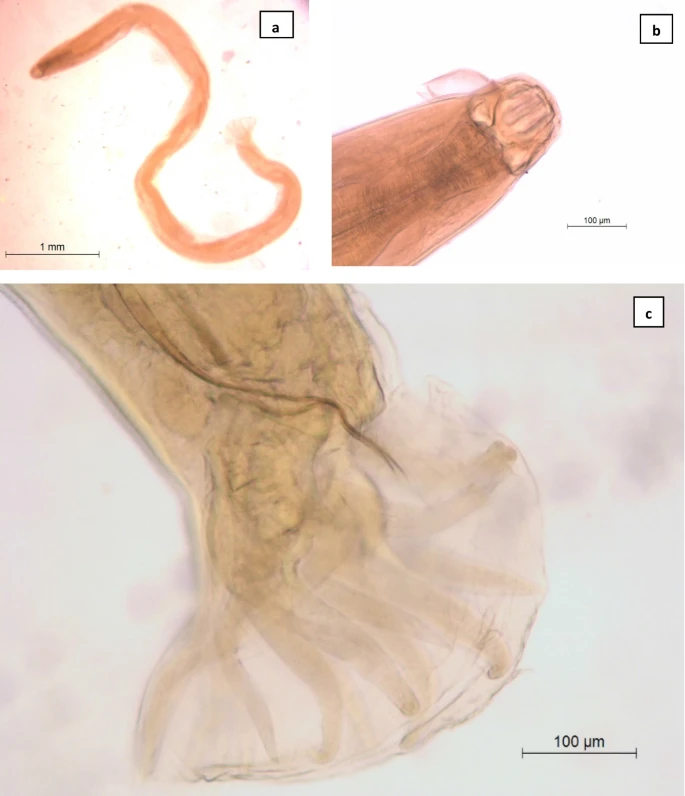
The helminth fauna present in the gut contents of Iberian adders, Vipera seoanei (Squamata: Viperidae), were characterised and analysed in respect to biological and eco-geographic factors that may affect the occurrence and diversity of helminths in this species. Leer más.
These findings further suggest that population historical demographic events influence hologenomic variation and provide new insights into how immunogenetic host variability and microbial diversity may jointly influence host fitness with consequences for disease susceptibility and population persistence. Leer más.

Our results provide important guidance on how to prioritize measures that incorporate climate change in decision-making processes related to the current and future management and protection of marine turtles at the ocean-basin scale, and could be used to guide decisions in other regions globally. Leer más.
